BFF - Backend For Frontend

Implementing a Backend for Frontend Pattern
The backend for frontend (BFF) pattern has become popular in recent years as a way to build scalable and maintainable web applications. A BFF provides a tailored API layer that sits between the frontend and backend services.
What is a Backend for Frontend?
A backend for frontend is a layer that sits between the frontend and backend services. It is designed to handle requests from specific frontend frameworks or platforms. The BFF abstracts away the general-purpose backend APIs to provide an API tailored for each frontend client.
Some key benefits of using a BFF include:
-
Customization - The BFF can transform backend responses into a format optimized for each frontend. This avoids cluttering up the frontend code (Over fetching and Over requesting)
-
Security - The BFF acts as a security layer, protecting the backend from unwanted requests. It can implement authentication, authorization and rate limiting.
-
Performance - The BFF can cache requests and undertake request collapsing to optimize performance for the frontend.
-
Separation of concerns - The backend services focus on business logic while the BFF focuses on interfacing with frontends. This separation makes both the backends and frontends easier to understand and maintain.
-
Independent evolution - The backend services and frontend clients can evolve independently without affecting each other by making changes in the BFF layer.
Implementing a BFF
There are several approaches for implementing a BFF:
-
Serverless functions - Functions as a Service like AWS Lambda can handle requests and run custom logic for each frontend.
-
API gateway - An API gateway sits in front of backend services and can transform, secure and optimize requests.
-
Dedicated BFF server - Build a dedicated BFF application, often using Node and Express, to handle frontend requests.
-
Microservices - Each BFF can be deployed as an independent microservice to handle one or more frontends.
The implementation should focus on:
- Authentication and authorization
- Customizing responses for the frontend
- Caching and request collapsing
- Rate limiting policies
- Logging, monitoring and analytics
Proper testing is key to ensure the BFF reliably interfaces with both the frontend clients and backend services as they independently change.
| Without BFF | With BFF |
|---|---|
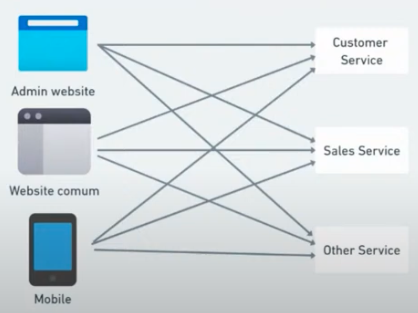 |
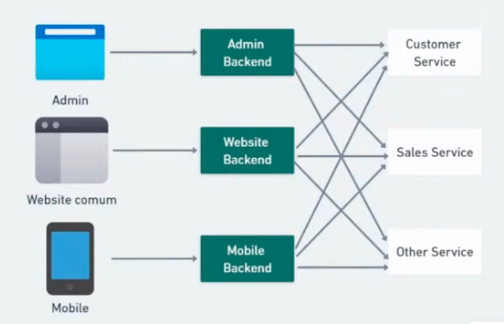 |
Conclusion
The backend for frontend pattern is useful for modern web and mobile applications with diverse frontends. Implementing a well-designed BFF provides performance, security, and maintainability benefits. However, it does introduce additional complexity that should be carefully managed.
References
https://samnewman.io/patterns/architectural/bff/#
https://www.sensedia.com.br/post/utilizacao-de-graphql-como-implementacao-do-padrao-bff